实用医学杂志 ›› 2025, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (13): 1987-1996.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2025.13.007
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-03-28
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-07-18
通讯作者:
徐军明
E-mail:xjmsh@hotmail.com
基金资助:Received:2025-03-28
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-07-18
Contact:
Junming XU
E-mail:xjmsh@hotmail.com
摘要:
目的 探究基质金属蛋白酶19(MMP-19)在结直肠癌(CRC)及肝转移(CRLM)中的功能及分子机制。 方法 整合并分析TCGA、GEO数据库中CRC及CRLM患者的转录组、单细胞数据与临床资料。通过RNA测序数据分析与MMP-19表达相关的生物学功能,并采用qRT-PCR、Western blot和免疫组织化学染色检测MMP-19在原发灶与肝转移灶中的表达差异。此外,通过体外功能实验验证MMP-19对结直肠癌细胞增殖、侵袭及迁移的作用。 结果 MMP-19在CRC组织中呈高表达,且与CRC、CRLM患者的不良预后显著相关。测序结果及功能富集分析表明MMP-19参与上皮间质转化、氨基酸蛋白转运、细胞增殖、细胞外基质组织构成及MAPK信号通路等生物学功能。单细胞分析显示在CRC原发灶及肝转移灶中,MMP-19在巨噬细胞和树突状细胞的表达高于正常组织。体外实验证实,MMP-19可增强结直肠癌细胞的增殖、侵袭及迁移能力。 结论 MMP-19可能通过诱导上皮间质转化及重塑免疫微环境,促进CRC的发生发展及增加术后复发及肝转移风险,有望成为CRC、CRLM诊断和治疗的新靶点。
中图分类号:
何泽平,徐军明. 基质金属蛋白酶19在结直肠癌及其肝转移中的作用与预后价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(13): 1987-1996.
Zeping HE,Junming XU. The role and prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinase 19 in colorectal cancer and its liver metastasis[J]. The Journal of Practical Medicine, 2025, 41(13): 1987-1996.
表1
GSE164522数据集分析MMP-19在CRLM免疫微环境中的表达 (x ± s)"
| 组别 | 细胞类型 | 细胞占比 | MMP-19 | F值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肝转移灶 | 巨噬细胞 | 0.49 | 0.84 ± 1.04a | 1 125.38 | 8.08e-234 |
| 肝转移灶旁正常组织 | 0.17 | 0.26 ± 0.66 | |||
| 原发位结直肠癌 | 0.22 | 0.41 ± 0.88b | 24.44 | 7.95e-07 | |
| 原发癌旁正常组织 | 0.15 | 0.27 ± 0.72 | |||
| 肝转移灶 | 树突状细胞 | 0.23 | 0.33 ± 0.72c | 190.874 | 7.247e-43 |
| 肝转移灶旁正常组织 | 0.10 | 0.13 ± 0.44 | |||
| 原发位结直肠癌 | 0.23 | 0.33 ± 0.73d | 6.492 | 0.01 | |
| 原发癌旁正常组织 | 0.15 | 0.21 ± 0.59 |
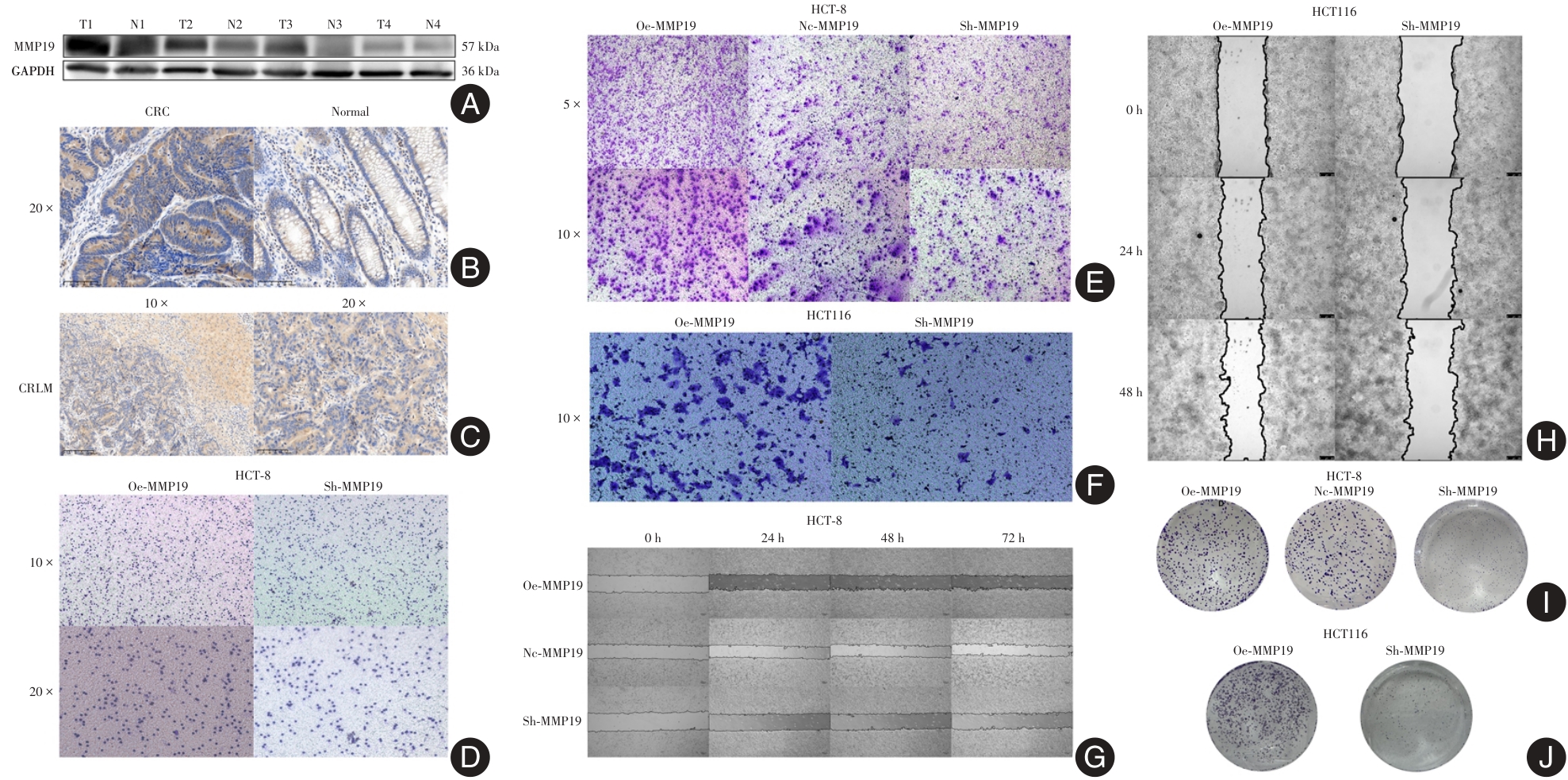
图 4
MMP-19在CRC与CRLM组织中的表达及细胞功能实验验证注:A,Western Blot验证CRC组织中MMP-19的表达;B,IHC验证CRC组织中MMP-19的表达(免疫组织化学染色);C,IHC验证CRLM组织中MMP-19的表达(免疫组织化学染色);D,Transwell实验验证MMP-19促进HCT-8细胞的侵袭(结晶紫染色);E,Transwell实验验证MMP-19促进HCT-8细胞的迁移(结晶紫染色);F,Transwell实验验证MMP-19促进HCT116细胞的迁移(结晶紫染色);G,划痕愈合实验验证MMP-19促进HCT-8细胞的迁移;H,划痕愈合实验验证MMP-19促进HCT116细胞的迁移;I,平板克隆形成实验验证MMP-19促进HCT-8细胞的增殖(结晶紫染色);J,平板克隆形成实验验证MMP-19促进HCT116细胞的增殖(结晶紫染色)"
| [1] | YAN C, SHAN F, LI Z Y. [Prevalence of colorectal cancer in 2020: A comparative analysis between China and the world] [J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2023, 45(3): 221-229. |
| [2] |
ZHOU H, LIU Z, WANG Y, et al. Colorectal liver metastasis: Molecular mechanism and interventional therapy [J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 70. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00922-2
doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00922-2 |
| [3] |
PETRONI G, BUQUE A, COUSSENS L M, et al. Targeting oncogene and non-oncogene addiction to inflame the tumour microenvironment [J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2022, 21(6): 440-462. doi:10.1038/s41573-022-00415-5
doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00415-5 |
| [4] |
PEZESHKIAN Z, NOBILI S, PEYRAVIAN N, et al. Insights into the Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Precancerous Conditions and in Colorectal Cancer [J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(24):6226. doi:10.3390/cancers13246226
doi: 10.3390/cancers13246226 |
| [5] |
ZHAO W, WANG L, YANG J, et al. Endothelial cell-derived MMP19 promotes pulmonary fibrosis by inducing E(nd)MT and monocyte infiltration [J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 56. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01040-4
doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01040-4 |
| [6] |
DAI C, XU P, LIU S, et al. Long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 affects paclitaxel and cisplatin resistance by regulating MMP19 in epithelial ovarian cancer cells [J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2021, 303(5): 1271-1281. doi:10.1007/s00404-020-05858-y
doi: 10.1007/s00404-020-05858-y |
| [7] |
MULLER M, BECK I M, GADESMANN J, et al. MMP19 is upregulated during melanoma progression and increases invasion of melanoma cells [J]. Mod Pathol, 2010, 23(4): 511-521. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.183
doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2009.183 |
| [8] |
LETTAU I, HATTERMANN K, HELD-FEINDT J, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-19 is highly expressed in astroglial tumors and promotes invasion of glioma cells [J]. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 2010, 69(3): 215-223. doi:10.1097/nen.0b013e3181ce9f67
doi: 10.1097/nen.0b013e3181ce9f67 |
| [9] |
LU J, KORNMANN M, TRAUB B. Role of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(19):14815. doi:10.3390/ijms241914815
doi: 10.3390/ijms241914815 |
| [10] |
SINGH M, MORRIS V K, BANDEY I N, et al. Advancements in combining targeted therapy and immunotherapy for colorectal cancer [J]. Trends Cancer, 2024, 10(7): 598-609. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2024.05.001
doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2024.05.001 |
| [11] |
PARKHURST M, GOFF S L, LOWERY F J, et al. Adoptive transfer of personalized neoantigen-reactive TCR-transduced T cells in metastatic colorectal cancer: phase 2 trial interim results [J]. Nat Med, 2024, 30(9): 2586-2595. doi:10.1038/s41591-024-03109-0
doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03109-0 |
| [12] |
PITTAYAPRUEK P, MEEPHANSAN J, PRAPAPAN O, et al. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Photoaging and Photocarcinogenesis [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016, 17(6):868. doi:10.3390/ijms17060868
doi: 10.3390/ijms17060868 |
| [13] |
SHOARI A, ASHJA ARDALAN A, DIMESA A M, et al. Targeting Invasion: The Role of MMP-2 and MMP-9 Inhibition in Colorectal Cancer Therapy [J]. Biomolecules, 2024, 15(1):35. doi:10.3390/biom15010035
doi: 10.3390/biom15010035 |
| [14] |
MENG LI M W. Expression and Clinical Characteristics of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Malignant Tu-mors [J]. Advances in Clinical Medicine, 2022, 12(05): 4355-60. doi:10.12677/acm.2022.125631
doi: 10.12677/acm.2022.125631 |
| [15] |
CRAIG V J, ZHANG L, HAGOOD J S, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases as therapeutic targets for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2015, 53(5): 585-600. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2015-0020tr
doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0020tr |
| [16] |
YANG C, DONG X, SUN B, et al. Physical immune escape: Weakened mechanical communication leads to escape of metastatic colorectal carcinoma cells from macrophages [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2024, 121(22): e2322479121. doi:10.1073/pnas.2322479121
doi: 10.1073/pnas.2322479121 |
| [17] |
CHEN H, ZHAI C, XU X, et al. Multilevel Heterogeneity of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis [J]. Cancers (Basel), 2023, 16(1):59. doi:10.3390/cancers16010059
doi: 10.3390/cancers16010059 |
| [18] |
SHASHA T, GRUIJS M, VAN EGMOND M. Mechanisms of colorectal liver metastasis development [J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2022, 79(12): 607. doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04630-6
doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04630-6 |
| [19] |
LIU C, QU L, ZHAO C, et al. Extracellular gamma-synuclein promotes tumor cell motility by activating beta1 integrin-focal adhesion kinase signaling pathway and increasing matrix metalloproteinase-24, -2 protein secretion [J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 117. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0783-6
doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0783-6 |
| [20] |
WANG Y, YU S J, LI Y X, et al. Expression and clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase-17 and -25 in gastric cancer [J]. Oncol Lett, 2015, 9(2): 671-676. doi:10.3892/ol.2014.2747
doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2747 |
| [21] |
XIAO C, WANG Y, CHENG Q, et al. Increased expression of MMP17 predicts poor clinical outcomes in epithelial ovarian cancer patients [J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2022, 101(34): e30279. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000030279
doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000030279 |
| [22] |
ZHANG Y, WANG J, FAN Y, et al. MMP11 and MMP17 are potential biomarkers for uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma prognosis [J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2024, 26(3): 653-663. doi:10.1007/s12094-023-03284-5
doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03284-5 |
| [23] |
YU J, HE Z, HE X, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of the Expression and Prognosis for MMPs in Human Colorectal Cancer [J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 771099. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.771099
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.771099 |
| [24] |
MI T, ZHANG Z, ZHANGHUANG C, et al. Doxycycline hydrochloride inhibits the progress of malignant rhabdoid tumor of kidney by targeting MMP17 and MMP1 through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway [J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2024, 964: 176291. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176291
doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176291 |
| [25] |
YIP C, FOIDART P, SOMJA J, et al. MT4-MMP and EGFR expression levels are key biomarkers for breast cancer patient response to chemotherapy and erlotinib [J]. Br J Cancer, 2017, 116(6): 742-751. doi:10.1038/bjc.2017.23
doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.23 |
| [26] |
PAOLILLO M, SCHINELLI S. Extracellular Matrix Alterations in Metastatic Processes [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(19):4947. doi:10.3390/ijms20194947
doi: 10.3390/ijms20194947 |
| [27] |
JIROUSKOVA M, ZBODAKOVA O, GREGOR M, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of MMP-19 deficiency in a mouse model of chronic liver fibrosis [J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(10): e46271. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046271
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046271 |
| [1] | 吴娜,张泽天,王锐. B7族同源体3、过氧化物酶1、硫氧还蛋白在溃疡性结肠炎及其相关性结直肠癌患者血清和组织中的表达及意义[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(9): 1407-1412. |
| [2] | 王立坤,郝琦,金炜涵,董时正,武雪亮,胡晓峰,武亮,荀敬,马洪庆. 多组学与人工智能在预测和诊断结直肠癌肝转移中的应用[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(7): 1070-1078. |
| [3] | 孔蔺莎,何改改,李婷,方坤,何维,韦力. 磁性载药凝胶珠包裹阿霉素治疗结直肠癌的实验研究[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(7): 953-959. |
| [4] | 王伟,王敏,成敏敏,张婷婷. 红花多糖对结直肠癌小鼠肿瘤生长及磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B/雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(5): 670-675. |
| [5] | 朱吉玥,张波,李亚茹,黄留业. 全身炎症反应指数对早期结直肠癌内镜黏膜下剥离术后非治愈性切除的预测价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(5): 716-723. |
| [6] | 彭天忠,黄学娣,林星镇,袁娟,周峰,刘浪辉,占琦楠,朱满华. 开窍醒神针法联合加味补阳还五汤对脑出血恢复期患者(气虚血瘀证)IL-2、MMP-9、BDNF及脑血流量的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(3): 428-433. |
| [7] | 王龙,吴映敏,尚莎,王璐. 5'-tRF-GlyGCC在结直肠癌早期诊断价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(11): 1730-1735. |
| [8] | 杨潇,王涛,王伟,彭耀辉,陈妍,曾海平,杨宝. 结直肠癌患者的血清脂质组学特点及其诊断价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(11): 1742-1750. |
| [9] | 尚文颖,龙蝶,陈海辉. 联合临床病理特征和基因检测结果分析左右半结直肠癌差异的真实世界研究[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2025, 41(1): 48-52. |
| [10] | 丁宇轩,郭沥泞,沈佳怡,王丽君. 放疗联合PD-1抑制剂及酪氨酸激酶抑制剂治疗MSS型结直肠癌肝转移疗效及安全性[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(9): 1293-1297. |
| [11] | 王海英,吴凯,田胤纯. 血清基质金属蛋白酶-9、细胞角蛋白19片段及血管内皮细胞生长因子水平与非小细胞肺癌患者顺铂治疗效果的关系[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(24): 3452-3457. |
| [12] | 邓伟,彭丹,胡海军,张静,余树春,黄松. 伤害指数联合脑电双频指数监测下全身麻醉在腹腔镜结直肠癌根治术中的应用[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(24): 3476-3481. |
| [13] | 谭玲,马雪,王静静,雷丰丰. 基质金属蛋白酶-28在肺部疾病中的研究进展[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(20): 2949-2953. |
| [14] | 汤明欣,王晓林,李炫飞. 他汀类药物在结直肠癌防治中的研究进展[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(14): 2041-2046. |
| [15] | 于艳艳,康霞,范林林,张海峰,王晓龙,韦海涛,李丽. LINC00626通过JAK1/STAT3/KHSRP信号轴调控结直肠癌转移的恶性进展[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2024, 40(12): 1643-1650. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||


